Communicators
Visualising and summarising Bayesian model results
Communicators help you communicate your findings. They cover both tables and plots. Again there are a set of default communicators built into hibayes which you can select from.
Built-in Communicators
| Communicator | Purpose | Key Parameters |
|---|---|---|
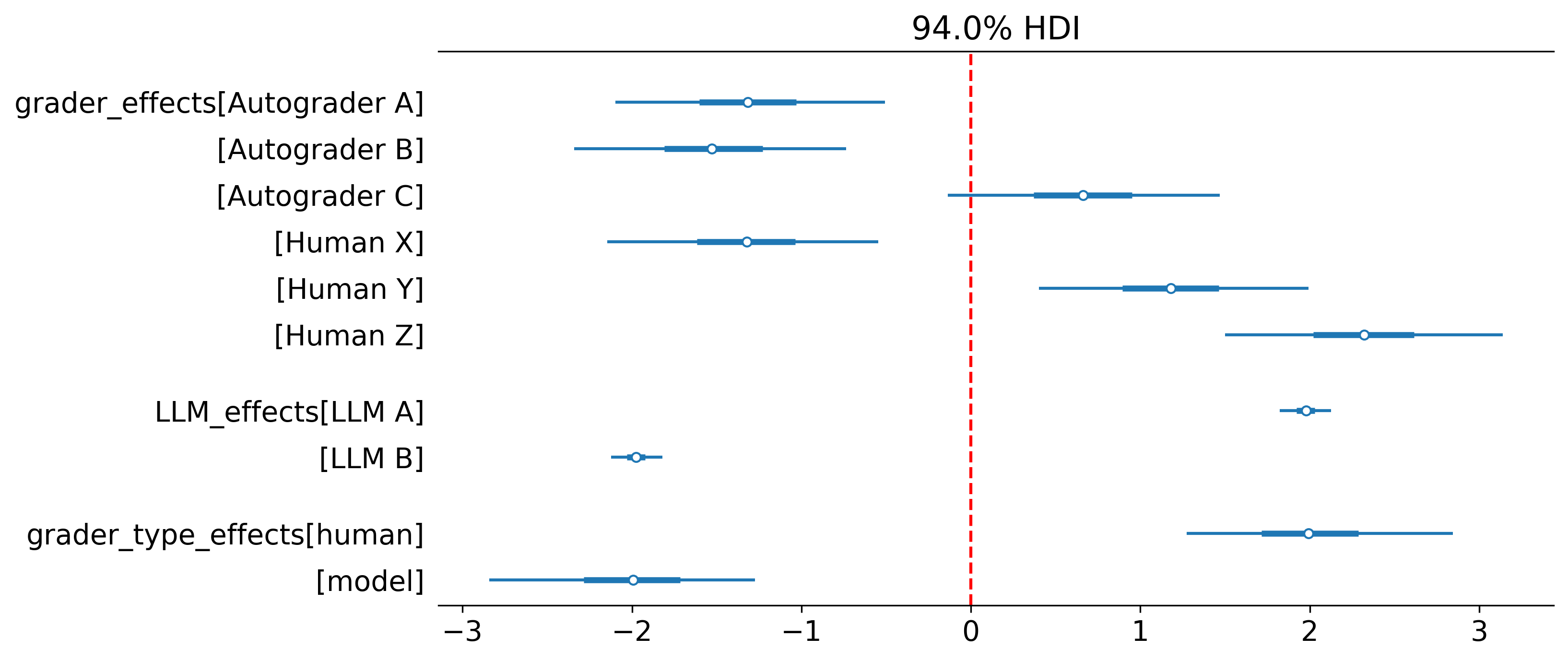
forest_plot |
Forest plot of parameter estimates with credible intervals | vars=None, vertical_line=None, best_model=True, transform=False |
trace_plot |
MCMC trace plots to assess convergence and mixing | vars=None, best_model=True, transform=False |
pair_plot |
Pairwise KDE plots showing parameter correlations | vars=None, best_model=True |
model_comparison_plot |
Compares models using information criteria (LOO/WAIC) | Requires ≥2 fitted models |
summary_table |
Statistical summary table of posterior parameters | vars=None, best_model=True, round_to=2 |
What makes up a communicator?
Communicators simply take in an AnalysisState and add a plot or a table. Here we see the implementation for a forest_plot, noting that you can define your own communicators using the same methodology
@communicate
def forest_plot(
vars: list[str] | None = None,
vertical_line: float | None = None,
best_model: bool = True,
figsize: tuple[int, int] = (10, 5),
transform: bool = False,
*args,
**kwargs,
):
def communicate(
state: AnalysisState,
display: ModellingDisplay | None = None,
) -> Tuple[AnalysisState, CommunicateResult]:
"""
Communicate the results of a model analysis.
"""
nonlocal vars
if best_model:
best_model_analysis = state.get_best_model()
if best_model_analysis is None:
raise ValueError("No best model found.")
models_to_run = [best_model_analysis]
else:
models_to_run = state.models
for model_analysis in models_to_run:
if model_analysis.is_fitted:
vars, dropped = (
drop_not_present_vars(vars, model_analysis.inference_data)
if vars
else (None, None)
)
if dropped and display:
display.logger.warning(
f"Variables {dropped} were not found in the model {model_analysis.model_name} inference data."
)
if vars is None:
vars = model_analysis.model_config.get_plot_params()
ax = az.plot_forest(
model_analysis.inference_data,
var_names=vars,
figsize=figsize,
transform=model_analysis.link_function if transform else None,
*args,
**kwargs,
)
if vertical_line is not None:
ax[0].axvline(
x=vertical_line,
color="red",
linestyle="--",
)
fig = plt.gcf()
state.add_plot(
plot=fig,
plot_name=f"model_{model_analysis.model_name}_{'-'.join(vars) if vars else ''}_forest",
)
return state, "pass"
return communicate- 1
- here we register the communicator and enforce an agreed upon interface.
- 2
- very useful to have kwargs here, as the user often have their own plotting args they want passed on to the plt functions.
- 3
- if you only want to create plots for the model which fitted the model best according the information criterion specified. Otherwise plot for every model.
- 4
- add the plot to the analysis state. Check output dir for plots
Here is an example forest plot with default configs from skewed score example